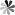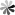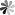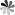Building Blocks for Liquid Crystals
Introduction
Liquid crystals can exhibit many phases, such as cholesteric, nematic and smectic, and ferroelectric. The phase state of the liquid crystal depends on the temperature of the substance and the properties of the material itself, that is, the composition, concentration, and molecular substituents.
The structure of liquid crystal affects the properties of liquid crystal, and the physical and chemical properties of materials can be analyzed from the perspective of molecular structure. As shown in Fig 1 below, the structure of liquid crystal molecules is generally composed of two parts, including a rigid main body and a flexible tail chain. The rigid main body is generally a core unit, and the core unit is usually composed of a ring system, which may be a benzene ring, or a heterocycle doped with nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, etc. If it is a benzene ring, it is generally called a benzene derivative. The core units can be connected directly or through simple rigid bridge bonds or groups, such as -CH=CH-, -COO-, -N=N-, etc., so as to ensure the rigidity of the backbone of the molecular structure. The flexible tail chain provided by R or R’ can lower the melting point of the liquid crystal material. The flexible tail chain is usually a straight-chain alkyl or long alkoxy chain. When the number of carbon atoms of the terminal alkyl group or alkoxy group is an odd number, it generally exhibits a liquid crystal state, and when the number is an even number, it generally does not exhibit a liquid crystal state.
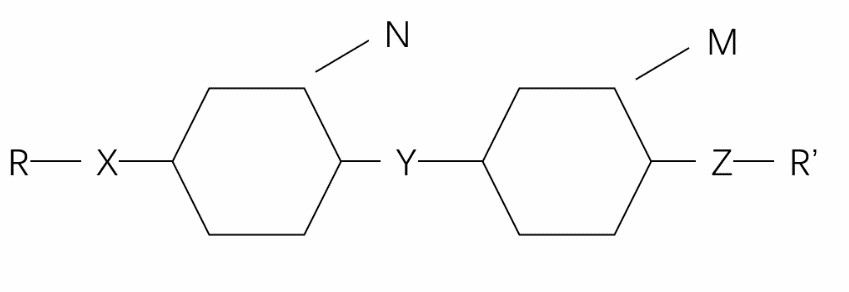 Fig 1 The structure of the liquid crystal molecule
Fig 1 The structure of the liquid crystal molecule
Application
Liquid crystal is a typical type of soft material that can realize self-assembly, and it is also a type of optoelectronic anisotropic material, which can respond to external stimuli such as light field, magnetic field, electric field, temperature, force, surface chemistry, etc.It is manifested as the change of the director of the liquid crystal molecule, and the physical properties of the substance, including changes in optics and electricity[1]. Therefore, it shows great application potential in many technical fields, including color displays, sensors, optical switches, Optical tuning optics, precise control of polarization, etc.
Reference
- Isogai M. Ferroelectric liquid crystals-physical properties and applications[J]. Solid State Physics.1985,20(7):481-488.